crude odds ratio calculator|Confounding and Effect Measure Modification : Cebu For two groups of subjects, each sorted according to the absence or presence of some .
Tanya Chinita was born on January 12, 1983 (age 41) in Cavite, Philippines. She is a Celebrity Radio Host. DJ and host known for her work on Love Radio Manila. She has over 320,000 followers on Instagram, 370,000 followers on Facebook and her eponymous YouTube channel's racked up over 27 million views.Discover (and save!) your own Pins on Pinterest.
PH0 · Odds Ratio: Formula, Calculating & Interpreting
PH1 · Odds Ratio Calculator
PH2 · Odds Ratio Calculation and Interpretation
PH3 · MedCalc's Odds ratio calculator
PH4 · Confounding and Effect Measure Modification
PH5 · Adjusted Odds Ratio: Definition + Examples
PH6 · Adjusted Odds Ratio
PH7 · 2x2 Contingency Table with Odds Ratios, etc.
The Boeing 777 is reported to be the world’s largest and most efficient jet. It is considered a unique plane due to its features. The plane has impressive range, fuel efficiency and provides .
crude odds ratio calculator*******The odds ratio (OR), its standard error and 95% confidence interval are calculated according to Altman, 1991. The odds ratio is given by with the standard error of the log odds ratio being and 95% confidence interval Where zeros cause problems with computation of the odds ratio or its standard error, 0.5 . Tingnan ang higit paMedCalc Software Ltd. Odds ratio calculator. https://www.medcalc.org/calc/odds_ratio.php (Version 22.026; accessed June 14, 2024) Tingnan ang higit paUse this odds ratio calculator to easily calculate the ratio of odds, confidence intervals and p-values for the odds ratio (OR) between an exposed and control group. One and two-sided confidence intervals are .
In this post, learn about ORs, including how to use the odds ratio formula to calculate them, different ways to arrange them for several types of studies, and how to interpret odds ratios and their confidence intervals .
Summary: Odds Ratio vs. Adjusted Odds Ratio. An odds ratio .For two groups of subjects, each sorted according to the absence or presence of some .
You calculate an overall crude (unadjusted) relative risk (or odds ratio) and compare it to the stratum-specific relative risks (or odds ratios). If the stratum-specific measures of association are similar to the crude .
crude odds ratio calculator Confounding and Effect Measure ModificationAOR is sometimes called a conditional odds ratio. In epidemiology, it’s sometimes called an Adjusted Disease Odds Ratio (ADOR). Un-adjusted vs. Adjusted Odds Ratios. Odds ratios can be adjusted, or un-adjusted (also called crude). In epidemiology, an un-adjusted OR will estimate the relative risk between a certain event in an exposed group .
logistic regression wifework. /method = enter inc. The equation shown obtains the predicted log (odds of wife working) = -6.2383 + inc * .6931 Let’s predict the log (odds of wife working) for income of $10k. -6.2383 + 10 * .6931 = .6927. We can take the exponential of this to convert the log odds to odds.
For a 2x2 Contingency Table: For two groups of subjects, each sorted according to the absence or presence of some particular characteristic or condition, this page will calculate standard measures for Rates, Risk Ratio, Odds, Odds Ratio, and Log Odds. It will also. perform the Fisher exact probability test, if the sample size is not too large.crude odds ratio calculatorA) Calculating Odds Ratios. We will calculate odds ratios (OR) using a two-by-two frequency table. Where. a = Number of exposed cases. b = Number of exposed non-cases. c = Number of unexposed cases. d = Number of unexposed non-cases. OR = .
And that will indeed show you the crude OR for your focal variable in Block 1 and an adjusted OR in Block 2. Here is an example using one of the "sample" datasets that comes with SPSS. NEW FILE .
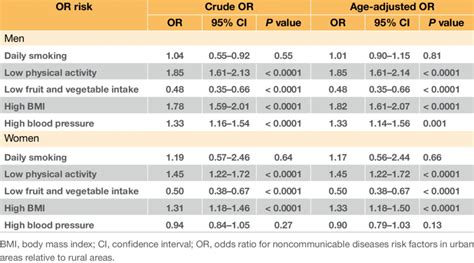
Confounding and Effect Measure ModificationBy more extreme, I mean that odds ratios that are greater than 1 will be larger than the corresponding risk ratio, and odds ratios that are less than 1 will be smaller than the corresponding risk ratio. The figure below depict shows that when the outcome is more common (e.g., >10%), the odds ratio exaggerates the estimated strength of association.The formula can also be presented as (a × d)/ (b × c) (this is called the cross-product). The result is the same: (17 × 248) = (15656/4216) = 3.71. The result of an odds ratio is interpreted as follows: The patients who received standard care died 3.71 times more often than patients treated with the new drug.Popular answers (1) The main difference between a crude odds ratio and an adjusted odds ratio is that the adjusted odds ratio is adjusted according to the other variables within a model. By .
Instructions: This calculator computes the Odds Ratio (OR) for a 2x2 crosstabulation, which measures the ratio of the odds of exhibiting a condition (or disease) for those in an exposed group, versus the the odds of exhibiting the condition (or disease) for those in the non-exposed group. Please type the 2x2 table data and also indicate the confidence .Crude and adjusted odds ratios (and 95% confidence intervals) from logistic regression analyses identifying associa-tions between selected characteristics and early sexual debut, by gender: Characteristic Male: Female Crude .Notice that the adjusted relative risk and adjusted odds ratio, 1.44 and 1.52, are not equal to the unadjusted or crude relative risk and odds ratio, 1.78 and 1.93. . For example, if one were to calculate the odds ratio . Odds ratio (OR) An odds ratio is a relative measure of effect, which allows the comparison of the intervention group of a study relative to the comparison or placebo group. So when researchers calculate an odds ratio they do it like this: The numerator is the odds in the intervention arm. The denominator is the odds in the control or placebo .The research design of an odds ratio is set up like below. Research Design and the 2x2 table. When researchers use a retrospective case-control design, the odds ratio with 95% confidence interval is used as the .The odds of a control being a smoker is 650/59 or 11.0. The odds ratio is 32.8/11.0, which is 3.0. Prism reports the value more precisely as 2.974 with a 95% confidence interval ranging from 1.787 to 4.950. You can interpret this odds ratio as a relative risk. The risk of a smoker getting lung cancer is about three times the risk of a nonsmoker . Here is how to interpret the results: Age: The adjusted odds ratio for age is calculated as e.045 = 1.046. This means the odds of having a baby with low birthweight are increased by 4.6% for each additional yearly increase in age, assuming the variable smoking is held constant. For example, suppose mother A and mother B are both smokers.

odds ratios are the measure of association in a case control study. This video demonstrates the calculation of the ORAn odds ratio (OR) is a statistic that quantifies the strength of the association between two events, A and B. The odds ratio is defined as the ratio of the odds of A in the presence of B and the odds of A in the absence of B, or equivalently (due to symmetry), the ratio of the odds of B in the presence of A and the odds of B in the absence of A.Two events are . The unadjusted or crude relative risk was RR = 1.78, and the unadjusted or crude odds ratio was OR =1.93. We also determined that age was a confounder, and using the Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel method, we estimated an adjusted relative risk of RR CMH =1.44 and an adjusted odds ratio of OR CMH =1.52. We will now use logistic .
Emirates NBA Cup, Group Play: 12 matchups to watch Here are 12 matchups to circle on your calendar when the tournament tips on Nov. 12. Offseason Power Rankings: State of West
crude odds ratio calculator|Confounding and Effect Measure Modification